The current online subspace requires users to be on their toes and keep themselves safe from online threats. Tools like VPN, DNS, and variations like Smart DNS and Encrypted DNS have become fairly popular in recent times.
Recently, there has been an ongoing debate on the functionalities of VPN, DNS, and other online tools. With overlapping features, people are often confused about the difference between VPN and Encrypted DNS.
If you are having trouble understanding how a DNS works and how it is different from a VPN, read our guide as we have explained each search tool bit by bit with its features and working process.
Quick Overview of DNS
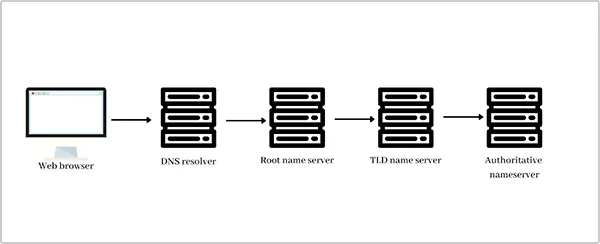
DNS stands for Domain Name System, which serves as the browser’s address directory, keeping a record of all domain names. Each time you enter a domain such as www.hey.com, the browser converts it into an IP address and subsequently links to the website, email server, and additional services. It has a record of all internet data and is highly unencrypted.
Furthermore, the DNS process lets users access websites without having to memorize the long numerical addresses. The first DNS was designed in 1987, and since then everyone from your Internet Service Provider (ISPs), to transit providers, and responders could see and modify your queries and responses.
Distinctive Features of DNS
Simply put, DNS works as an application layer protocol by utilizing User Data Protocol (UDP). Apart from translating human-friendly domain names into IP addresses, a DNS serves the following features:
- It supports dynamic updates to automatically adjust the available IP address mappings from devices on a given network every time an IP address changes.
- Furthermore, it ensures a greater level of security by safeguarding against Distributed Denial of Service Attacks.
- It is particularly used in load balancing to provide more than one IP address for a similar domain name.
How Does a DNS Work?
When you input a website URL in your browser, a DNS request is initiated to locate the desired IP address. This request is usually transmitted in plaintext, rendering it vulnerable to capture by harmful individuals or monitoring organizations. These vulnerabilities may result in privacy violations or cyberattacks.
DNS does wonders for its users, but it fails to provide them optimal security, as anyone can decrypt the network data and see the search history. This creates a big problem for internet users as their privacy is severely compromised.
To prevent anonymous users from peeping into your activity, an advanced version of the DNS system was introduced. As DNS is exposed to cyberattacks, a shield of privacy is provided to it to protect the user’s identity, which is called Encrypted DNS.
Let’s understand more about it in the next section.
What is Encrypted DNS?
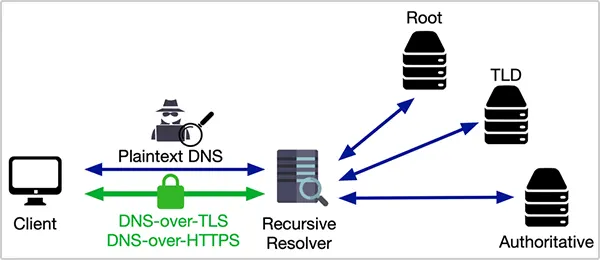
Encrypted DNS is also the basic DNS system but with enhanced privacy and security. This advanced model encrypts the DNS queries and does not allow foreign websites to view the activities. The traditional DNS queries are unencrypted, but in this, the requests are secured in the tunnel and prevent all kinds of interception.
The DNS network is encrypted via various methods and each of them gives different protection. These methods are:
- DNS over HTTPS: This is a method that uses HTTPS protocol to encrypt the queries. To enable DoH, you need to enter chrome://flags/#dns-over-https and set up the Secure DNS system.
- DNS over TLS: This method improves the privacy between the client and the resolver. Meaning, that your ISPs, and resolving network companies won’t be able to view your data because of DNS over the TLS system.
- DNSCrypt: This is a protocol that encrypts, verifies, and anonymizes the communication network between the DNS client and the DNS resolver. It is easy to install, high-performance, and run on zero maintenance proxy.
Key Features of Encrypted DNS
DNS networks are often confused with VPN, as both hide the IP Addresses and shield users’ identity. However, there’s a difference Between VPN And Encrypted DNS. Here are some key features that set it apart from the latter;
- Privacy Safeguard: Encrypting DNS requests stops ISPs and other middlemen from monitoring your online behavior.
- Lowered Chance of Manipulation: Encrypted DNS aids in blocking DNS spoofing attacks, during which attackers send you to harmful websites.
- Compatibility: Encrypted DNS can be deployed with minimal modifications to the current infrastructure.
How Does an Encrypted DNS Work?
As mentioned above, an Encrypted DNS translates the plain text DNS information into the encrypted one so that only your device and the DNS resolver can decipher the data exchanged. It effectively shields all your DNS queries from third parties and prevents your online privacy by scrambling all the related information sent during the domain name resolution process.
Due to this extended protection feature, many people confuse a DNS with a VPN, but they are poles apart from each other. Scroll to the next section for detailed information about VPNs.
Quick Overview of VPN
VPN stands for Virtual Private Network, its job is to create a safe network environment connection to the internet. When using a public network, you are prone to viruses and malware. However, VPN service establishes a secure surrounding by encrypting internet traffic.
Not only that, it lets you access content and websites from all over the world. A big difference between a VPN and Encrypted DNS is that a VPN lets you access geo-restricted content in just a single click. By encrypting your IP address and giving you a new one, a VPN can change your location. This allows you to access content that is restricted in your country and also stay protected from hackers. You can easily find many good VPN services like Urban VPN and McAffee VPN on the internet offering the best features. Also, you can explore different Residential VPN or free VPNs for a seamless experience.
Key Features of VPN
A VPN is a perfect tool for maintaining privacy on the internet, it also provides some extra features like location changing and access to specialized servers. Here are all the key features that you will find in a VPN:
- Encrypts your IP address and gives you a new IP from its server to protect your online identity.
- Protects your search data by making it unreadable by any third parties.
- Allows you to access restricted websites in your area by geo-spoofing.
- Provides data authentication to completely protect your internet searches and data.
How Does a VPN Work?
A VPN works by giving you a new IP address from its specialized servers. Its first job is to create a secure connection between your device and its servers. Most VPNs have hundreds of servers all around the world. The number of servers is directly proportional to how great the service of a VPN will be as a higher number of servers indicates better access to the internet due to low network congestion and higher internet speed.
After connecting to a VPN, your data will be routed from their dedicated servers, thereby changing your location. By tunneling your data, a VPN will also encrypt your data from any outside eyes.
Now that you know how a VPN and DNS work, you know how different they are. Next, we have given a comparison table between the two.
Check Out: Why is My VPN Not Connecting? – Causes and 10 Fixes
Difference Between VPN and Encrypted DNS
| Parameter | VPN | Encrypted DNS |
| Full Form | Virtual Private Network | Domain Name System |
| Purpose | Encrypts all internet traffic and routes it from a separate server. | Encrypts your DNS queries preventing anyone from seeing what you are searching for. |
| Privacy | Offers strong online protection and anonymity. | Offers moderate online protection as it doesn’t protect your complete internet search history. |
| Internet Speed | Significantly slows your internet speed due to connection with the extra server. | Minimal decline in internet speed as only search queries are encrypted. |
| Cost | High cost due to features. | Moderate cost, |
| Protocol in Use | IPSec, L2TP, ESP | DNS over HTTPS, UDP |
These are all the parameters that make a VPN different from an Encrypted DNS. With the emergence of smart and encrypted DNS, many people often confuse these with VPN. Now that we have defined and differentiated both terms, you will be able to use them effectively and correctly.
So this was all about DNS, Encrypted DNS, and VPN servers. We hope this blog has pointed out all the primary differences and their functioning properly. Share the info with your friends and family to help them protect their online identity too!
Read Next: What is VPN on my Phone? (Answered): Guide to Smartphone VPN
FAQs
1: Is Encrypted DNS an alternative to VPN?
Ans: No, an Encrypted DNS can’t be an alternative to a VPN as both have different features than each other. A VPN is used to protect your internet search history and a DNS is used for only protecting the DNS requests.
2: Which is better, Private DNS or VPN?
Ans: VPN is considered to be better than Private DNS and other versions of DNS, but it depends on what your needs are to find a better alternative. For some users, DNS can be a better and more effective option than VPN.
3: Can I use Encrypted DNS and VPN at the same time?
Ans: Yes, you can use both Encrypted DNS and VPN at the same time, but it is not recommended to do so as a VPN already encrypts your DNS requests.
4: Does VPN protect against DNS?
Ans: Yes, a VPN does protect your DNS requests and secures your internet data properly.
Sources
DNS, VPN, and Smart DNS: Which is Right for You? – By NordVPN

